"External BGP (EBGP) Route Propagation Behavior without Policies” was published as RFC 8112 . What does this mean for network operators and vendors?
After a bit of tug-of-war common sense prevailed and RFC 8212 “External BGP (EBGP) Route Propagation Behavior without Policies” was published at https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8212.
This industry has a long history of improving default behaviour: DEC MOP is no longer enabled by default, telnet was swapped out in favor of SSH, and SHA-1 is now deprecated, so I’m confident we can manage this one too.
TL;DR This article offers advice on test scenarios to add to your evaluation checklist and a call to action to ask your vendor to implement RFC 8212. Please share this message with other communities.
Background
Prior to RFC 8212, the default behaviour of BGP implementations (when no policy is configured on an EBGP session) was undefined, this resulted in a myriad of vendor defaults: some implementations not accepting routes and not advertising anything; some would accept anything, but announce nothing; some would announce only internal routes and accept anything; and some would indiscriminately accept everything and announce everything. The latter mode of operation is of course the most harmful one.
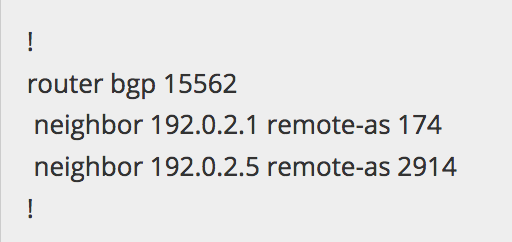
An example minimal configuration:
!
router bgp 15562
neighbor 192.0.2.1 remote-as 174
neighbor 192.0.2.5 remote-as 2914
!
Most of us have learned (the hard way) that on many platforms the above configuration will not only bring up two BGP sessions, but also immediately result in a “Lateral ISP-ISP-ISP Leak”, simply because no routing policy was associated with these EBGP sessions and an implicit ‘permit-any’ is assumed. The above configuration is of course an oversimplification of what happens in real life: operators may attempt to change a BGP peer to a peer-group which has missing configuration, or a copy+paste of a snippet of configuration only partially succeeds, or in an attempt to debug a BGP session some configuration is removed without realising the full ramifications of doing so (until you see smoke coming off the circuit ;-).
RFC 8212 updates the core BGP specification (RFC 4271) to specify that the above behaviour is incorrect, and an implicit deny-all must be associated with the EBGP session. In other words: “fail closed” rather then “fail open and oops you tripped max-prefix all over the place (or worse)”.
The document purposefully does not cover IBGP, nor does it proscribe what the contents of configured policy on EBGP sessions should be. If an operator explicitly configures a ‘permit-any’ style policy, that is perfectly fine, it was a conscious choice to do so.
Evaluation checklist
Going forward when you evaluate a BGP implementation or a new software release, it is advisable to take note of the default behaviour of that specific release. As vendors come into compliance with RFC 8212 it may be beneficial to track this. I also strongly recommend to audit your network configurations for instances which depend on implicit ‘permit-any’ behavior and reconfigure those instances to be an explicit ‘permit-any’. This way software upgrades are less likely to cause surprises, and as a bonus the readability of the device’s configuration is improved!
Call to action
Some vendors will need encouragement to take their implementation from EBGP “fail open” to “fail closed”, we are keeping track of the industry’s current state of affairs here: https://github.com/bgp/RFC8212
Please contact your account management team and express your interest in them supporting RFC 8212. Also, make sure to include RFC 8212 in your next round of “Request for Proposals” (RFPs) as a ‘must have’. Purchasing usually is an excellent opportunity to have meaningful dialogue with the vendor.
Some vendors may argue “But our customers depend on our unsafe behaviour!”, but this only holds true if we don’t speak up collectively and show them otherwise. EBGP is an Internet-wide shared resource, we all benefit from sane defaults.
Hat tip to Jared Mauch for initiating this project and to Greg Hankins for demonstrating change is possible.



Comments 0
The comments section is closed for articles published more than a year ago. If you'd like to inform us of any issues, please contact us.