
Echoes
• 4 min read
Recently, we spotted a network bug that had precisely the opposite of the intended effect.

Articles
Likes on articles

Stephen is a principal engineer in the Office of the CTO at Fastly, where he spends his time trying to figure out what the Internet is. He obtained his PhD in Internet routing scalability from the University of Glasgow in 2012.

• 8 min read
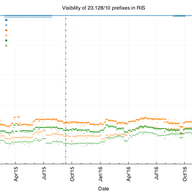
Since October 2014, we have been advertising two IPv4 /25s and two IPv4 /28s, to better understand how far they propagate across the network. In this article, we review how things have (or have not) changed over the years.

• 7 min read
Last week, the Network Traffic, Measurement and Analysis Conference (TMA) took place in Maynooth, Ireland. A full week was scheduled, featuring a PhD school across Monday and Tuesday, the Mobile Network Measurements (MNM) workshop on Tuesday, and the main conference from Wednesday to Friday. We wer…

• 9 min read
Last month we covered the 2015 leap second ahead of the insertion of a leap second at the very end of 2016. As stated previously, leap seconds can trigger poorly-tested code paths; leap second handling always unearths bugs and issues. This one was no exception!

• 8 min read
On 31 December this year, we're scheduled for another leap second. There are many stories about what leap seconds can do to infrastructure and applications, and rituals are built up around them. Such rituals stem from reality: leap seconds trigger poorly-tested code paths and run contrary to assump…

• 7 min read
With IPv4 address space depleted, it's increasingly important to transition to IPv6. IPv6 transition mechanisms, which allow the two protocols to interoperate, can help. One such mechanism is NAT64. We use RIPE Atlas to measure the usage of NAT64, and compare NAT64 paths to native IPv4 paths.
• 3 min read
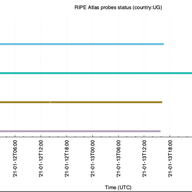
Reports indicate that the Ugandan government initiated a shutdown of the country's Internet yesterday evening. Here's a look at what we're seeing based on data available from our Routing Information Service (RIS) and RIPE Atlas.
• 8 min read
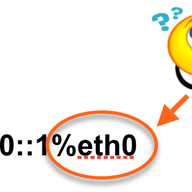
...or, how RIPE Atlas measurement data just got a little bit more complex. Some people say IPv6 is "96 more bits, no magic". And while this is true for most network operators, if you're a RIPE Atlas system programmer, you can run into interesting situations. In this article, we described how link-l…
• 11 min read
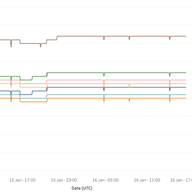
We are getting ready to start allocating from 2a10::/12, a new block of IPv6 addresses. In this process we did a couple of 'pre-flight' checks to check the usability of address space in this /12 block.

• 7 min read
This year's Internet Measurement Conference (IMC) was held in Amsterdam from 21-23 October. In this article we highlight some of the presented work that we think is interesting and that the RIPE community might find useful.
• 8 min read
On-path load balancing can send traffic across many potential paths, which typical traceroute usage will not fully capture. We are working on algorithms for a more complete traceroute across load-balanced paths, and we are interested in deployment on RIPE Atlas. We'd like your feedback.

• 16 min read
The Internet Measurement Conference (IMC) is an annual conference focusing on Internet measurement and analysis. The 17th edition is taking place from 31 October to 2 November 2018 in Boston. RIPE NCC staff at the event will be live blogging key moments. See this page for regular updates on the iss…

• 7 min read
Network measurements are an important tool in understanding the Internet. Due to the expanse of the IPv6 address space, exhaustive scans in IPv4 are not possible for IPv6. The best practice when conducting IPv6 measurements is to use so called IPv6 hitlists.
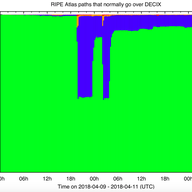
• 6 min read
On the night of 9 April 2018, DE-CIX Frankfurt experienced an outage. As this is one of the largest Internet Exchange Points, this is an interesting case to study in more depth to see what we can learn about Internet robustness. We plan to update this article if new information/corrections flow in.

• 40 min read
The 101st meeting of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) runs from 17 - 23 March 2018 in London. RIPE NCC staff at the event will be live blogging key moments. See this page for regular updates on the issues, arguments and ideas discussed over the course of the meeting.
Hey! The difference is that the .bz2 is a dump of measurement results, but /api/v2/measurements/traceroute/ gives you measurement metadata. The json returned from the API call you provided includes 'result' fields, each of which refers to the measurement IDs with the actual results. If you want, you can run through those pointers and pull down the measurement results manually to get at the result data we're putting into the .bz2 archives. Note also that the output of that API call is paginated; use option "page_size=500" (the maximum) to reduce the number of pages you have to loop over. Hope that helps!
“So, historic data older than one month will be lost (or made unuvailable publically) forever?”
Hi Alexander! Measurement data -- all of it -- is always available via the API. The archives discussed here are a convenience method, offering data from recent public measurements in bulk form. In the future, we may modify this service to hold data for longer or to provide samples of older data, in the same location. If so, we'll be sure to announce it.
“Hi, all. Is there a recommendation (RFC or something) that ISPs follow for allow or not allow and propagate longer than /24 prefixes?”
Hi Alan! I'm not personally aware of a document, only the common convention that has been accepted for many years. Many documents refer to the current practice, including https://www.ripe.net/publications/docs/ripe-399 (from 2006) and https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4116 (from 2005). A more recent look at how far /24s propagate on the v4 Internet was published here: https://labs.ripe.net/Members/stephen_strowes/bgp-even-more-specifics-in-2017 In practice, the convention exists to avoid bumping into routing table limits too soon; even natural growth rates using the current conventions can catch networks unawares; for example, https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/08/internet-routers-hitting-512k-limit-some-become-unreliable/
“Do you mean 6rd seriously? We live in year 2017 and you are using a technique for lazy people.”
Hi Thomas; we tend to take the view that reachability via an ISP-provisioned and managed transition mechanism is better than no reachability. Anything that brings more IPv6 to the internet is good.
Of course, the IPv6 world offers much finer granularity. A /32 ought to give folks 2^16 globally routable prefixes, so a maximum y-resolution of 65,536 pixels. x-resolution only relies on how patient the artist is!
Showing 5 comment(s)